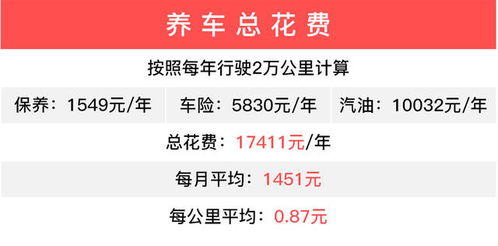
区块链受什么影响
Title: The Future of Blockchain: A Look into its Potential Adoption
Introduction:
Blockchain technology has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize various industries. However, the question of its widespread adoption remains a topic of debate. In this article, we will delve into the factors influencing the adoption of blockchain technology and provide insights into its potential future.
Understanding Blockchain:
Before discussing its adoption, it's essential to understand what blockchain technology entails. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures transparency, security, and immutability. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure and interconnected network.
Factors Influencing Adoption:
Several factors influence the widespread adoption of blockchain technology:
1.
Regulatory Environment:
Regulatory uncertainty poses a significant challenge to blockchain adoption. Governments worldwide are still grappling with how to regulate blockchainbased transactions, which impacts the willingness of businesses to integrate this technology into their operations.2.
Scalability:
Scalability issues, such as limited transaction throughput and high energy consumption in proofofwork consensus mechanisms, hinder blockchain's ability to handle largescale transactions efficiently. Addressing scalability concerns is crucial for blockchain to be viable for widespread adoption.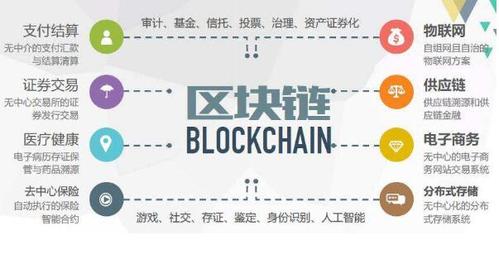
3.
Interoperability:
The lack of interoperability between different blockchain platforms and networks limits their utility. Seamless integration and communication between various blockchain ecosystems are essential for enabling comprehensive solutions and widespread adoption.4.
User Experience:
Improving the user experience is critical for mainstream adoption. Blockchain applications must be intuitive, secure, and accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise. Simplifying processes and enhancing user interfaces can drive adoption across diverse demographics.5.
Privacy and Security:
Ensuring data privacy and security is paramount for blockchain adoption, especially in industries dealing with sensitive information like finance and healthcare. Advancements in privacypreserving technologies and robust security protocols are necessary to instill trust in blockchain solutions.Potential Applications:
Despite these challenges, blockchain technology holds immense potential across various industries:
1.
Finance:
Blockchain has already disrupted the financial sector with applications like cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi). These innovations offer opportunities for faster, cheaper, and more transparent financial transactions, reducing reliance on intermediaries.2.
Supply Chain Management:
Blockchain enables endtoend traceability and transparency in supply chains, helping organizations track the flow of goods and verify product authenticity. This enhances efficiency, reduces fraud, and improves trust among stakeholders.3.
Healthcare:
In healthcare, blockchain can streamline processes like patient record management, prescription tracking, and clinical trials. By securely storing and sharing medical data, blockchain enhances data integrity, interoperability, and patient privacy.4.
Governance and Voting:
Blockchainbased voting systems can enhance the integrity and transparency of elections by providing immutable records of voter participation and ensuring tamperproof ballots. This could address concerns related to electoral fraud and enhance democratic processes.Conclusion:
In conclusion, the widespread adoption of blockchain technology hinges on addressing various challenges, including regulatory hurdles, scalability issues, interoperability concerns, and user experience improvements. Despite these challenges, blockchain holds immense potential to revolutionize industries such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and governance. By overcoming barriers and embracing innovation, stakeholders can unlock the full benefits of blockchain technology and usher in a new era of transparency, efficiency, and trust.
References:
Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A PeertoPeer Electronic Cash System. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
Tapscott, D., & Tapscott, A. (2016). Blockchain Revolution: How the Technology Behind Bitcoin Is Changing Money, Business, and the World. Penguin.
Swan, M. (2015). Blockchain: Blueprint for a New Economy. O'Reilly Media.