区块链能用在政务哪个领域
Title: Leveraging Blockchain in Electronic Governance Projects
2.
Transparency and Accountability:
The transparent nature of blockchain promotes accountability in government transactions. Citizens can track the flow of funds and monitor the allocation of resources, fostering trust in government processes.While blockchain offers promising solutions for egovernance, several challenges must be addressed:
Challenges and Considerations
Introduction
Conclusion
3.
Security:
Cryptographic algorithms ensure the integrity and security of transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.2.
Collaborate with Stakeholders:
Collaboration with stakeholders, including government agencies, technology providers, academia, and civil society organizations, is crucial for the success of egovernance projects. Stakeholders should be involved in the design, development, and implementation phases to ensure alignment with user needs and regulatory requirements.4.
Citizen Empowerment:
Blockchain enables citizens to participate directly in decisionmaking processes through secure voting mechanisms. By decentralizing voting systems, blockchain enhances the integrity and transparency of elections, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.5.
Infrastructure Requirements:
Deploying blockchain infrastructure requires significant investment in hardware, software, and technical expertise. Governments should assess their infrastructure readiness and develop robust deployment strategies to maximize the benefits of blockchain technology.Integrating blockchain technology into egovernance projects offers several advantages:
1.
Scalability:
Blockchain networks face scalability issues, particularly in handling large volumes of transactions. Implementers must choose scalable blockchain platforms capable of accommodating the demands of egovernance applications.4.
Decentralization:
The absence of a central authority distributes control among network participants, eliminating single points of failure.3.
Regulatory Compliance:
Egovernance projects must comply with regulatory frameworks governing data protection, privacy, and cybersecurity. Implementers should address legal and regulatory challenges to ensure compliance and mitigate risks.1.
Transparency:
All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, accessible to all participants, ensuring transparency and accountability.Successful implementation of blockchain in egovernance projects requires careful planning and execution:
In recent years, blockchain technology has gained significant attention for its potential to revolutionize various industries, including electronic governance (egovernance). Egovernance aims to enhance the efficiency, transparency, and accountability of government services through digital solutions. This article explores the benefits, challenges, and implementation strategies of utilizing blockchain in egovernance projects.
Blockchain technology holds immense potential to transform egovernance by enhancing transparency, accountability, and efficiency in government operations. By leveraging blockchain, governments can improve service delivery, empower citizens, and build trust in public institutions. However, successful implementation requires overcoming various challenges, including scalability, interoperability, regulatory compliance, user education, and infrastructure requirements. With careful planning, collaboration, and investment, blockchainbased egovernance projects can pave the way for a more inclusive and participatory democracy.
Implementation Strategies
4.
Invest in Infrastructure:
Governments must invest in the necessary infrastructure, including blockchain platforms, network infrastructure, and cybersecurity measures. Cloudbased solutions and blockchainasaservice offerings can help reduce infrastructure costs and complexity.1.
Data Integrity and Security:
Blockchain ensures the integrity and security of sensitive government data by storing it in an immutable ledger. This reduces the risk of data tampering and unauthorized access, enhancing trust among citizens.2.
Interoperability:
Integrating blockchain with existing government systems and protocols requires interoperability standards. Collaborative efforts among government agencies and technology providers are essential to ensure seamless integration and data exchange.5.
Promote Awareness and Adoption:
Governments should launch awareness campaigns to educate citizens, businesses, and public officials about the benefits of blockchain technology in egovernance. Training programs, workshops, and community engagement initiatives can foster a culture of innovation and collaboration.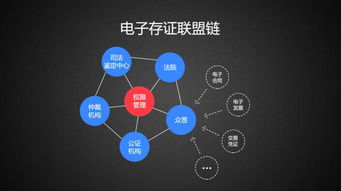
4.
User Education and Adoption:
Blockchain technology is complex, requiring users to understand its principles and functionalities. Governments must invest in user education and training programs to facilitate the adoption of blockchainbased egovernance solutions.3.
Pilot Projects:
Governments should start with smallscale pilot projects to test the feasibility and effectiveness of blockchain solutions in realworld scenarios. Pilot projects enable iterative development and refinement based on user feedback and performance evaluation.3.
Streamlined Processes:
Blockchainbased smart contracts automate and streamline administrative processes, reducing bureaucracy and operational costs. Smart contracts execute predefined actions automatically when certain conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries.Blockchain is a decentralized, immutable ledger technology that enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. It operates on a distributed network of nodes, where each transaction is recorded in a block, cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming a chain. Key features of blockchain include:
2.
Immutability:
Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a tamperproof record of activities.Understanding Blockchain Technology
5.
Fraud Prevention:
The immutability of blockchain prevents fraudulent activities such as identity theft, corruption, and vote manipulation. Government agencies can leverage blockchain to authenticate identities, verify credentials, and ensure the legitimacy of transactions.1.