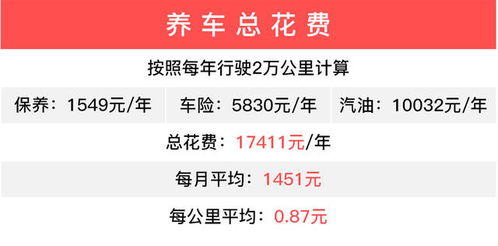
Title: Exploring the Uncharted Frontiers of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, while already transformative in various sectors, continues to evolve, presenting new challenges and opportunities for innovation. To navigate these uncharted frontiers, it's essential to understand the key areas where blockchain technology can make significant breakthroughs:
Scalability remains a paramount challenge for blockchain networks. As the number of transactions increases, traditional blockchains face bottlenecks in processing speed and throughput. To address this, researchers and developers are exploring various solutions such as:
- Layer 2 solutions like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and state channels for Ethereum.
- Sharding, which involves partitioning the blockchain into smaller segments to parallelize transaction processing.
- Optimized consensus algorithms like Proof of Stake (PoS) and delegated Proof of Stake (dPoS) to enhance network efficiency.
Interoperability is crucial for realizing the full potential of blockchain technology. Achieving seamless communication and data exchange between different blockchain networks and traditional systems remains a challenge. Key initiatives to enhance interoperability include:
- Interoperability protocols such as Polkadot and Cosmos, which aim to create an internet of blockchains.
- Atomic swaps and crosschain smart contracts to enable trustless exchange of assets across disparate blockchains.
- Standardization efforts by organizations like the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA) and Hyperledger to establish common frameworks.
While blockchain offers transparency and immutability, ensuring privacy and confidentiality of sensitive data on public ledgers remains a challenge, particularly in industries like finance and healthcare. Promising approaches to address this include:
- Zeroknowledge proofs (ZKPs) and homomorphic encryption to enable private transactions and computations on public blockchains.
- Privacyfocused blockchains like Monero and Zcash, which prioritize anonymity features.
- Layer 2 solutions like Aztec and Tornado Cash, providing privacy enhancements for Ethereum transactions.
The energy consumption associated with blockchain mining, particularly in Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, raises concerns about its environmental impact. To make blockchain technology more sustainable, efforts are underway to:
- Transition to alternative consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA) that require less energy.
- Explore energyefficient mining techniques and renewable energy sources for powering blockchain networks.
- Develop ecofriendly blockchain platforms such as Algorand and Tezos that prioritize sustainability.
Regulatory uncertainty poses a significant barrier to blockchain adoption, especially in heavily regulated industries like finance and healthcare. To foster compliance and regulatory clarity, stakeholders are working on:
- Engaging with policymakers and regulatory bodies to develop clear guidelines and frameworks for blockchain implementation.
- Implementing robust identity verification and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures to adhere to antimoney laundering (AML) and counterterrorism financing (CTF) regulations.
- Utilizing blockchain analytics tools to ensure transparency and traceability of transactions, addressing concerns related to illicit activities.
In conclusion, while blockchain technology has made remarkable strides, there are still numerous challenges to overcome to unlock its full potential. By addressing scalability, interoperability, privacy, sustainability, and regulatory compliance, the blockchain ecosystem can pave the way for broader adoption and impactful innovation across industries.